原题说明
Given the root of a binary tree, consider all root to leaf paths: paths from the root to any leaf. (A leaf is a node with no children.)
A node is insufficient if every such root to leaf path intersecting this node has sum strictly less than limit.
Delete all insufficient nodes simultaneously, and return the root of the resulting binary tree.
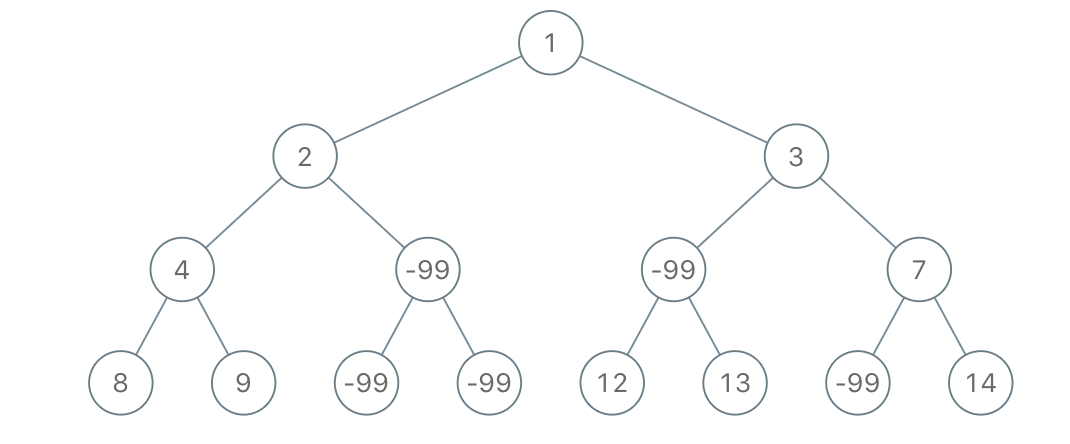
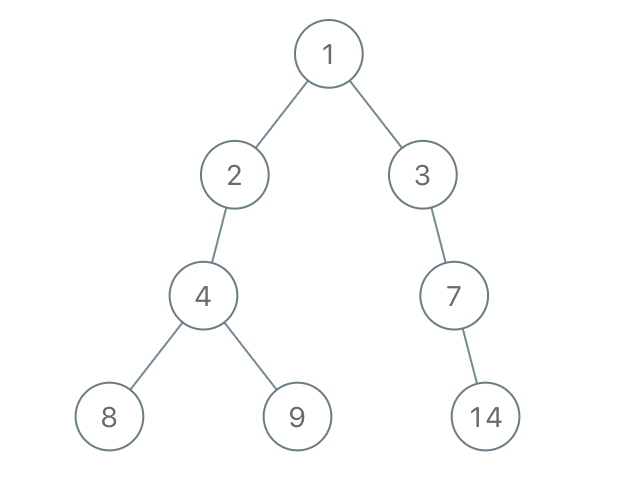
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,-99,-99,7,8,9,-99,-99,12,13,-99,14], limit = 1
Output: [1,2,3,4,null,null,7,8,9,null,14]
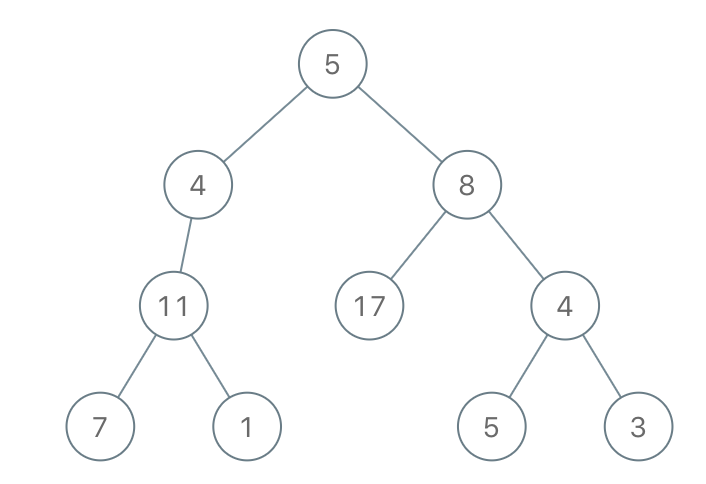
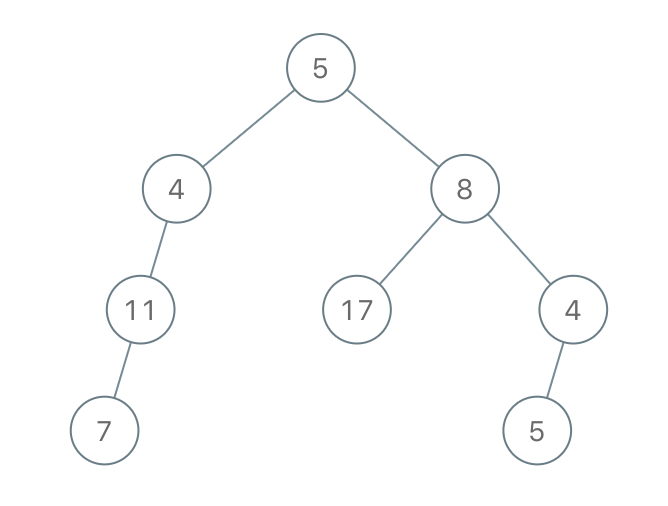
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,1,null,null,5,3], limit = 22
Output: [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,null,null,null,5]
Example 3:
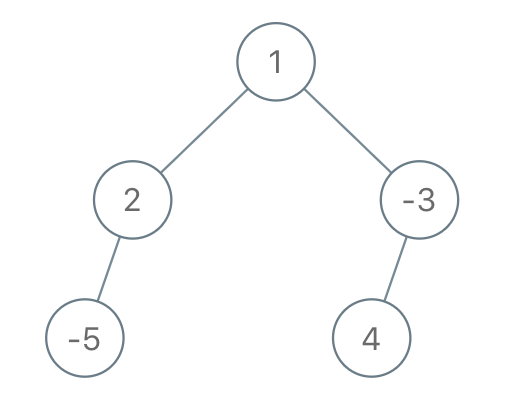
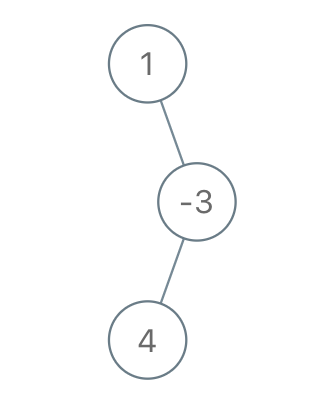
Input: root = [1,2,-3,-5,null,4,null], limit = -1
Output: [1,null,-3,4]
Note:
- The given tree will have between
1and5000nodes. -10^5 <= node.val <= 10^5-10^9 <= limit <= 10^9
解题思路
题目要去除所有不充分的点。这里对一个点是否充分的定义是:每一条从根节点开始,通过该点到达任意叶子节点的路径的和,都严格小于题目给出的值Limit。把所有不充分的点同时删除后,返回剩下的二叉树的根。
用dfs的方法解题,
- 当一个节点是叶子节点时,直接判断它是否是充分的,如果不是,返回
nullptr,否则返回该节点的指针。 - 当一个节点不是叶子节点时,判断它的子节点是不是都是不充分的。如果都是不充分的,那么返回
nullptr,也就是说它也是不充分的。否则返回该节点的指针。
工程上,C++可以选用smart pointer,从而不用考虑内存泄露的问题。
示例代码 (cpp)
1 | /** |
示例代码 (java)
1 | class Solution { |
示例代码 (python)
1 | class Solution(object): |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
视频讲解
我们在Youtube上更新了视频讲解,欢迎关注!