原题说明
Given the root of a binary search tree with distinct values, modify it so that every node has a new value equal to the sum of the values of the original tree that are greater than or equal to node.val.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
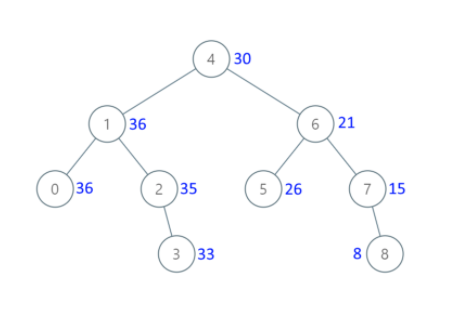
Input:
[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
Output:
[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is between 1 and 100.
Each node will have value between 0 and 100.
The given tree is a binary search tree.
Note: This question is the same as 538: https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
解题思路
题目要求将binary search tree中每个节点的值替换成不小于当前节点的所有元素的和。我们可以利用中序遍历的思想,进行发”反向“的中序遍历。也就是说将元素从大到小的进行搜索。遍历过程中,用一个变量记录到当前节点位置为止,所遍历过的元素的和。将其与当前节点的值进行替换。
代码可以用recursion和iteration两种方法实现。这里使用iteration的方法.优点在于,一是加深对中序遍历的理解, 二是避免stack overflow。
示例代码 (cpp)
1 | /** |
示例代码 (java)
1 | /** |
示例代码 (python)
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
归纳总结
我们在Youtube上更新了视频讲解,欢迎关注!