原题说明
In a 1 million by 1 million grid, the coordinates of each grid square are (x, y) with 0 <= x, y < 10^6.
We start at the source square and want to reach the target square. Each move, we can walk to a 4-directionally adjacent square in the grid that isn’t in the given list of blocked squares.
Return true if and only if it is possible to reach the target square through a sequence of moves.
Example 1:
Input: blocked = [[0,1],[1,0]], source = [0,0], target = [0,2]
Output: false
Explanation: The target square is inaccessible starting from the source square, because we can’t walk outside the grid.
Example 2:
Input: blocked = [], source = [0,0], target = [999999,999999]
Output: true
Explanation: Because there are no blocked cells, it’s possible to reach the target square.
Note:
0 <= blocked.length <= 200blocked[i].length == 20 <= blocked[i][j] < 10^6source.length == target.length == 20 <= source[i][j], target[i][j] < 10^6source != target
解题思路
题目给我们一个1百万乘1百万的迷宫,同时告诉你其中一些点是阻隔的,不能通过。问你是否有一条通路可以从点source连接到target。
按照常规思路,我们首先想到的肯定是用DFS或者BFS的方法,从一个点开始,暴力搜索所有能到的点。但是,由于迷宫非常大,这样做的时间复杂度会达到O(10^12),你提交的解法会 TLE。
我们回头仔细看题目给我们的Note, 发现blocked的长度是有限制的,最多不超过200。这能给我们带来启发。首先,两个点之所以不能联通,一定是因为被blocked中的点分隔开了。那意味着blocked中的点能将迷宫分割成两个部分,每个部分分别包含source和target中的一个点。而因为blocked的点数量不超过200,因此,它所能围城的面积也是有限制的。
我们可以将问题抽象成这样一个数学问题,在一个1000000 \* 1000000的矩形中,用一条长200的线,最多能围出多大的面积?这个问题可以用泛函的知识求解,这里不多做说明。但其实我们利用对称性可以知道,在任意一个角,围出一个弧长200的1/4圆就是最大的面积,也就是4/pi \* 10000。
知道了这个面积,我们只需要对source和target分别做两次BFS。每次BFS,我们设定所搜的次数不超过我们求出的这个最大面积。如果在这些点中找到了target或source,那自然说明有这样一条通路。否则:
- 如果我们发现
BFS在我们设定的搜索次数内,已经完成,那么说明source或者target处于被blocked点和迷宫边界构成的一个封闭区间内,不存在通路。 - 如果
BFS在设定的搜索次数内没有完成,说明并没有这样一个封闭区间能包裹住source或者target,那它们两个点一定是能够连通的。
下图给出target和source别阻隔时,可能的情况。(图片引子Discuss中2017111303的帖子)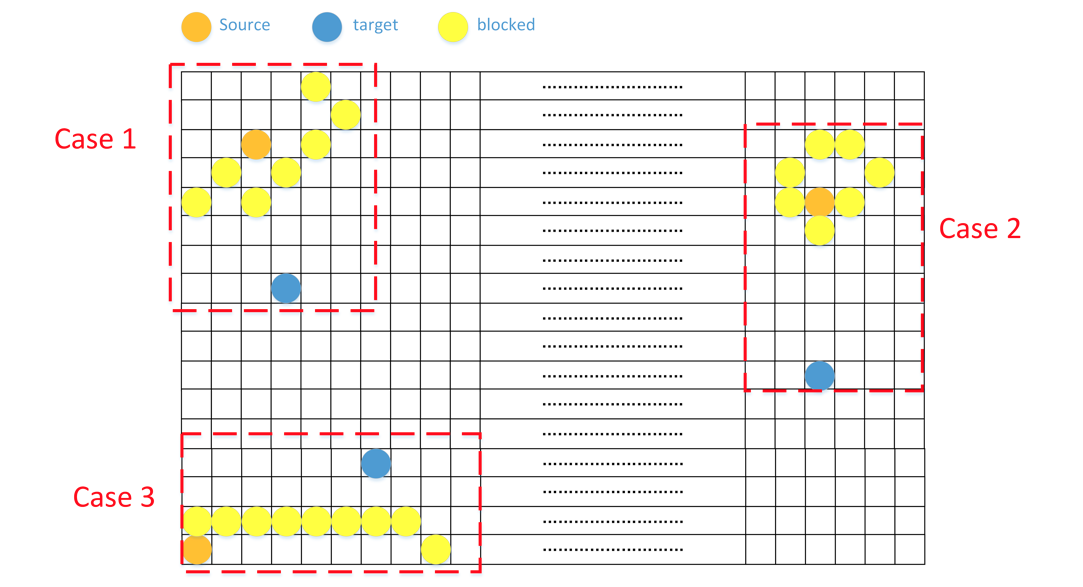
示例代码 (cpp)
1 | class Solution { |
示例代码 (java)
1 | class Solution { |
示例代码 (python)
1 | class Solution(object): |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(len(blocked)^2)
空间复杂度: O(len(blocked))
归纳总结
我们在Youtube上更新了视频讲解,欢迎关注!
