原题说明
Given a 2-dimensional grid of integers, each value in the grid represents the color of the grid square at that location.
Two squares belong to the same connected component if and only if they have the same color and are next to each other in any of the 4 directions.
The border of a connected component is all the squares in the connected component that are either 4-directionally adjacent to a square not in the component, or on the boundary of the grid (the first or last row or column).
Given a square at location (r0, c0) in the grid and a color, color the border of the connected component of that square with the given color, and return the final grid.
解题思路
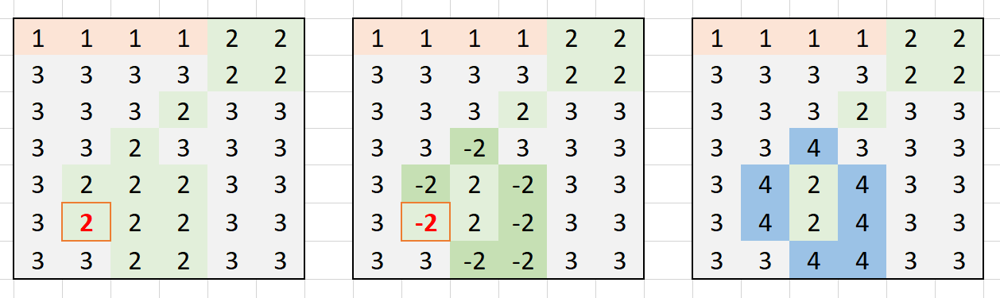
题目给我们一个坐标,要求将这个坐标表示的点所属的component的边界用给定的颜色标记出来。
我们用DFS的方法解决这道题。从给定的起点A开始,我们可以方便的遍历A所在的component的所有点。为了不开辟额空间,我们直接将A原来的颜色originColor翻转为-originColor。
那如何在找出边界呢?我们只需要在完成一个点上下左右四个方向的遍历之后,检查这个点是不是在component内部,在的话我们再次翻转-originColor,把它复原为originColor。经过这样的步骤之后,地图上所有标记为-originColor的点就是我们需要的边界了。我们将这些点重新标记为题目要求的color即可。
同学们可以看下图给出的例子有个具体认识(图片引自Discuss中votrubac的发帖)。
示例代码 (cpp)
1 | class Solution { |
示例代码 (java)
1 | class Solution { |
示例代码 (python)
1 | # python代码提供一种使用额外空间记录遍历点的方法 |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(N*M)
空间复杂度: O(1)N, M分别是grid的长和宽。
归纳总结
我们在Youtube上更新了视频讲解,欢迎关注!
