原题说明
We run a preorder depth first search on the root of a binary tree.
At each node in this traversal, we output D dashes (where D is the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. (If the depth of a node is D, the depth of its immediate child is D+1. The depth of the root node is 0.)
If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
Given the output S of this traversal, recover the tree and return its root.
Example 1: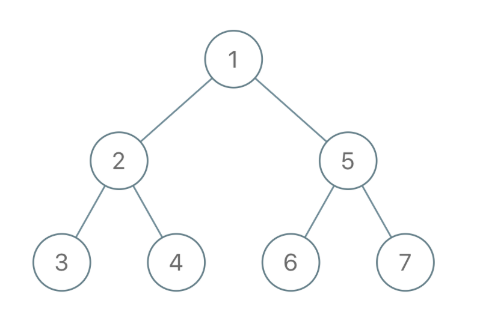
Input:
"1-2--3--4-5--6--7"
Output:[1,2,5,3,4,6,7]
Example 2:
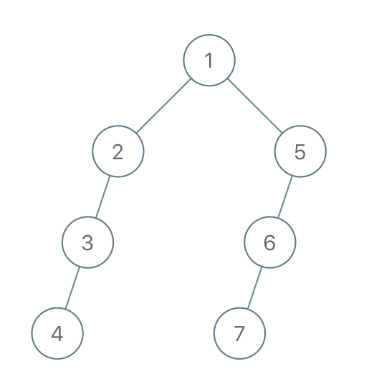
Input:
"1-2--3---4-5--6---7"
Output:[1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]
Example 3:
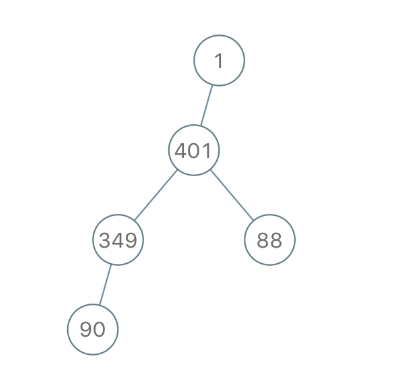
Input:
"1-401--349---90--88"
Output:[1,401,null,349,88,90]
解题思路
parse String S, 遍历获取每个node以及它对应的level。类似于用非递归法前序遍历二叉树,我们来重构二叉树。使用stack的数据结构(这里我们用vector代替stack,本质是一样的)。stack的size就是当前遍历到的二叉树的深度。当stack.size() > level时,意味着当前节点为根节点的子树都被遍历过了,需要退栈,直到stack.size == level,插入当前新遍历到的node。
最后返回stack[0], 即二叉树的根节点。
示例代码 (cpp)
1 | /** |
示例代码 (java)
1 | /** |
示例代码 (python)
1 | # Definition for a binary tree node. |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n)
归纳总结
我们在Youtube上更新了视频讲解,欢迎关注!
